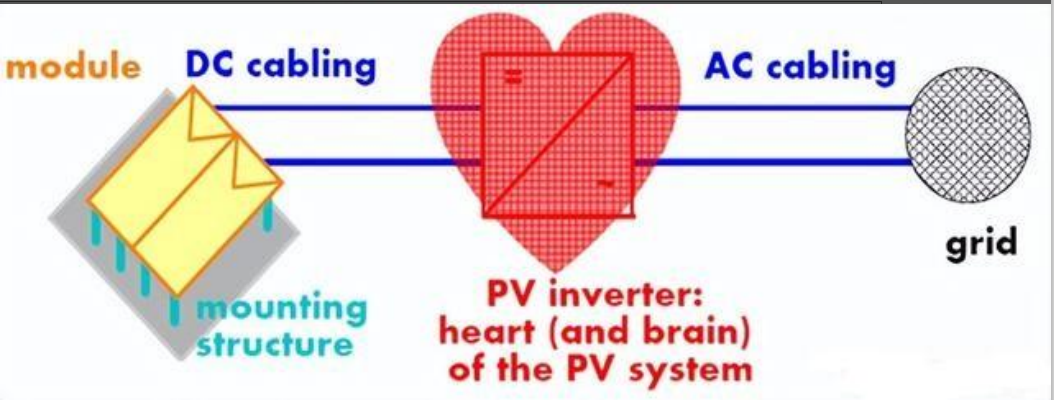
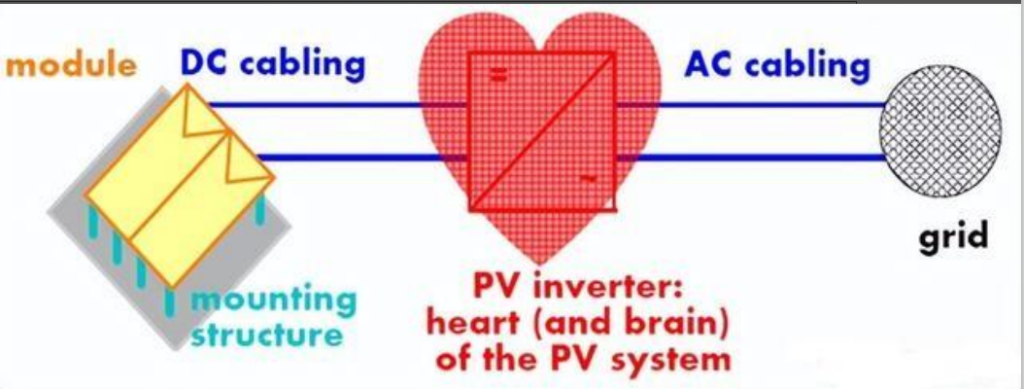
General knowledge about inverters
General knowledge about inverters :
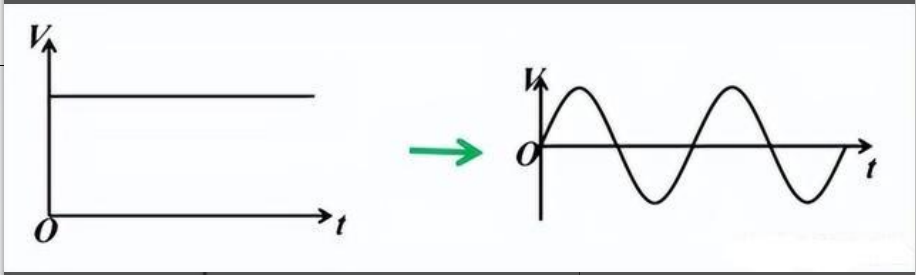
Inverters are devices that convert DC (direct current) power into AC (alternating current) power. They have numerous applications ranging from powering household appliances to providing electricity to electric grids. The main advantage of inverters is that they enable the use of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power which typically produce DC power. Moreover, they efficiently regulate the voltage and frequency of the AC power, thereby ensuring stable and clean energy supply. Inverters also play a key role in reducing carbon footprint and promoting sustainable living practices. Therefore, investing in inverters is a smart choice for a greener and more cost-effective energy future.
Main parameters and meaning of inverter:
- Maximum photovoltaic input power,Maximum DC input voltage,Rated DC current,MPPT voltage,Starting voltage
- Power Factor,Total current harmonic distortion,European efficiency,Output voltage range,Protection level,MPPT efficiency
The main components of the inverter can be divided into:
- Shell and terminals: used for wiring and protection
- Radiator: used for system heat dissipation of the inverter
- Display screen: Displays the status and data of the inverter
- Control board,: for internal power supply of the inverter
- Power panel: core components, inverter function control, various algorithm controls
- Power board: The core part, the main circuits are integrated on the power board
Photovoltaic power generation is a renewable energy source with great development potential. As an important part of photovoltaic power generation, the main function of photovoltaic inverter is to convert the direct current generated by photovoltaic modules into alternating current. Its functions include the regulation and management of the charging and discharging process of the battery system, the frequency adjustment and power balancing of the power grid, etc. The inverter itself does not generate any power. Its power or power is provided by the DC power supply.